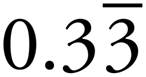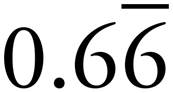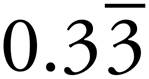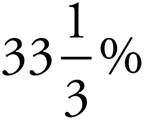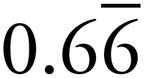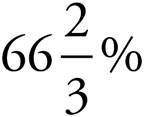SSAT & ISEE Prep 2023 - Princeton Review 2023
Answer key to fundamental math drills
The basics of both tests
The Building Blocks
Practice Drill 1—Math Vocabulary
1.6
0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
2.1, 3, 5
Many sets of integers would answer this question correctly.
3.3
3, 5, and 7
4.8
The tens digit is two places to the left of the decimal.
5.That number
The smallest positive integer is 1, and any number times 1 is equal to itself.
6.90
5 × 6 × 3 = 90
7.30
3 + 11 + 16 = 30
8.60
90 — 30 = 60
9.—6, —4, —2
2, 4, and 6 are consecutive positive even integers and the question wants negative. Other sets of consecutive negative even integers would also answer the question correctly.
10.Yes
11 is divisible only by 1 and itself.
11.22
5 + 6 + 4 + 7 = 22
12.6
13 goes into 58, 4 times. 4 × 13 = 52 and 58 — 52 = 6.
13.1, 5, 11, 55
1, 5, 11, and 55 will all divide into 55 evenly.
14.12
5 + 8 + 9 = 22 and 1 + 2 + 0 + 7 = 10.
22 — 10 = 12
15.No
The remainder of 19 ÷ 5 is 4. And 21 is not divisible by 4.
16.2, 2, 3, 13
Draw a factor tree.
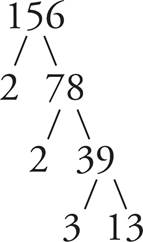
17.16
3 + 13 = 16
18.9
12 × 3 = 36 and 9 × 4 = 36.
19.1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9, 12, 18, 24, 36, 72
Remember that factors are the numbers that can be multiplied together to get 72.
20.There are 9 even factors and 3 odd factors.
The even factors are 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 18, 24, 36, and 72. The odd factors are 1, 3, and 9.
21.10
Add the values. 6 + 8 + 11 + 15 = 40. Then divide by the number of values. 40 ÷ 4 = 10.
Practice Drill 2—Adding and Subtracting Negative Numbers
1.—8
2.—14
3.— 4
4.27
5.21
6.4
7.—22
8.—29
9.—6
10.90
11.0
12.29
13.24
14.—30
15.—14
Practice Drill 3—Multiplying and Dividing Negative Numbers
1.— 4
2.—36
3.65
4.11
5.63
6.—13
7.84
8.—5
9.9
10.—8
11.—75
12.72
13.— 4
14.34
15.—11
Practice Drill 4—Order of Operations
1.9
Do addition and subtraction from left to right. 10 — 3 = 7, then 7 + 2 = 9.
2.16
Parentheses first! 7 — 3 = 4, then do addition and subtraction from left to right. 15 + 4 = 19, then 19 — 3 = 16.
3.7
Multiplication and division happen before addition and subtraction. 3 × 2 = 6 and 3 ÷ 3 = 1, then 6 + 1 = 7.
4.50
Parentheses, then exponents, then multiplication and division (from left to right). 4 + 6 = 10, then 10 squared is 100, then 2 × 100 = 200, and 200 ÷ 4 = 50.
5.6
Work inside the parentheses first, doing the multiplication before the addition. 5 x 12 = 60, then 10 + 60 = 70. 420 ÷ 70 = 6.
6.30
Multiplication and division first, from left to right, then addition. 20 × 5 = 100, then 100 ÷ 10 = 10, then 10 + 20 = 30.
7.24
Parentheses first, then multiplication and division (from left to right). 7 — 6 = 1, then 5 × 10 = 50, then 50 × 1 = 50, then 50 ÷ 2 = 25. Next do the addition and subtraction (from left to right). 3 + 25 = 28, and 28 — 4 = 24.
8.60
Parentheses first, then multiplication and division (from left to right). 8 + 1 = 9, 3 + 1 = 4, and 8 — 2 = 6. Then 10 × 9 = 90, 90 × 4 = 360, and 360 ÷ 6 = 60.
9.101
Parentheses, then exponents, then division, then addition and subtraction (from left to right). 5 × 2 = 10, 10 squared = 100. 33 ÷ 3 = 11. Then 12 + 100 = 112, and 112 — 11 = 101.
10.—200
Exponents first, then multiplication and division (from left to right), then subtraction. 23 = 8. 150 ÷ 3 = 50, and 50 × 8 = 400. Then 200 — 400 = —200.
Practice Drill 5—Factors and Multiples
1.2, 4, 6, 8, 10
4, 8, 12, 16, 20
5, 10, 15, 20, 25
11, 22, 33, 44, 55
2.Yes
3 goes into 15 evenly 5 times.
3.Yes
Use the divisibility rule for 3. The sum of the digits is 9, which is divisible by 3.
4.No
The sum of the digits is 14, which is not divisible by 3.
5.Yes
The only factors of 23 are 1 and 23.
6.Yes
The sum of the digits is 6, which is divisible by 3.
7.No
The sum of the digits is 6, which is not divisible by 9.
8.Yes
250 ends in a 0, which is an even number and is divisible by 2.
9.Yes
250 ends in a 0, which is divisible by 5.
10.Yes
250 ends in a 0, which is divisible by 10.
11.Yes
2 × 5 = 10
12.No
There is no integer that can be multiplied by 3 to equal 11.
13.No
2 is a factor of 8.
14.Yes
4 × 6 = 24
15.No
There is no integer that can be multiplied by 6 to equal 27.
16.Yes
3 × 9 = 27
17.8
6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48
18.8
Even multiples of 3 are really just multiples of 6.
19.8
Multiples of both 3 and 4 are also multiples of 12.
12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96
20.48
3 × 16 = 48
Practice Drill 6—Reducing Fractions
1. ![]()
2. ![]()
3. ![]()
4. ![]()
5. ![]()
6. ![]()
7. 1
8. 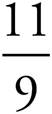
9. If the number on top is larger than the number on the bottom, the fraction is greater than 1.
Practice Drill 7—Changing Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers
1. 5
2. 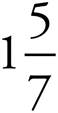
3. 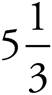
4. 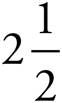
5. 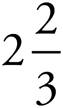
6. 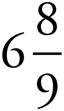
7. 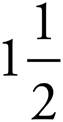
8. 2
9. 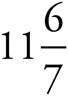
10. 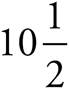
Practice Drill 8—Changing Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions
1. 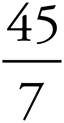
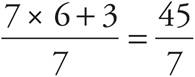
2. 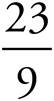
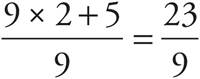
3. 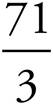
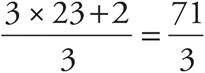
4. 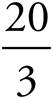
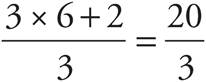
5. 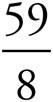
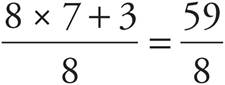
6. 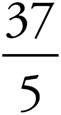
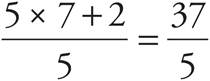
7. 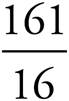
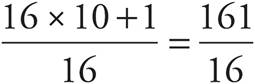
8. 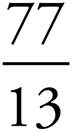
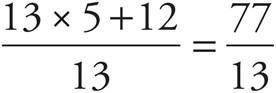
9. 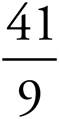
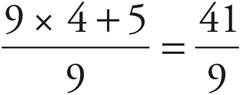
10. 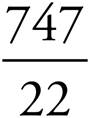
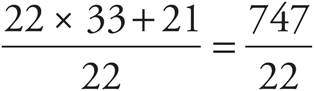
Practice Drill 9—Adding and Subtracting Fractions
1. 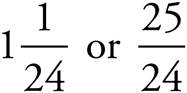
Multiply using Bowtie to get 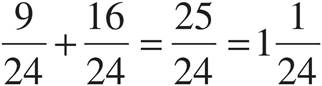 .
.
2. 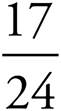
Multiply using Bowtie to get 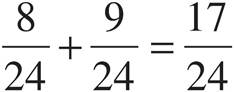 .
.
3. ![]()
Did you use the Bowtie? You didn’t need to because there was already a common denominator there!
4. 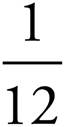
Multiply using Bowtie to get 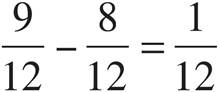 .
.
5. 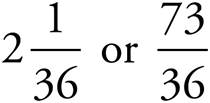
Multiply using Bowtie to get 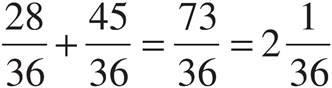 .
.
6. 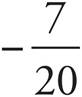
Multiply using Bowtie to get 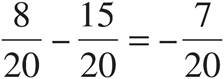 .
.
7. 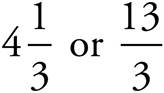
Multiply using Bowtie to get 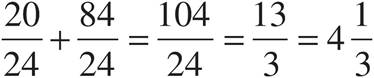 .
.
8. ![]()
Did you use the Bowtie? You didn’t need to because there was already a common denominator there! Subtract to get 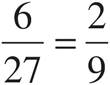 .
.
9. 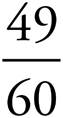
Multiply using Bowtie to get 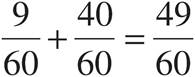 .
.
10. x
Multiply using Bowtie to get 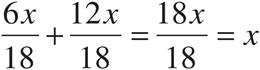 .
.
11. 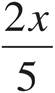
Multiply using Bowtie to get 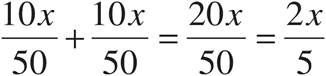 .
.
12. 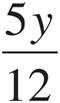
Multiply using Bowtie to get 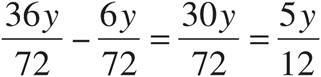 .
.
Practice Drill 10—Multiplying and Dividing Fractions
1. ![]()
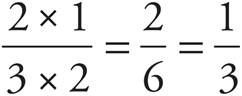
2. 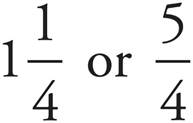
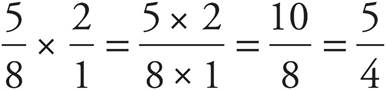
3. 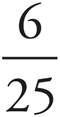
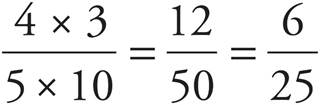
4. 1
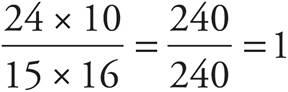
5. ![]()
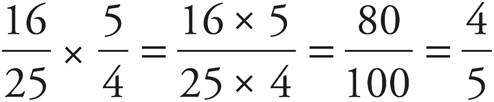
Practice Drill 11—Decimals
1.18.7
Don’t forget to line up the decimals. Then add.
2.4.19
After lining up the decimals, remember to add a 0 at the end of 1.7. Then add the two numbers.
3.4.962
Change 7 to 7.000, line up the decimals, and then subtract.
4.10.625
Don’t forget there are a total of 3 digits to the right of the decimals.
5.0.018
There are a total of 4 digits to the right of the decimals, but you do not have to write the final 0 in 0.0180.
6.6,000
Remember to move both decimals right 2 places: 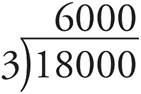 and don’t put the decimals back after dividing!
and don’t put the decimals back after dividing!
7.5
Remember to move both decimals right 2 places: 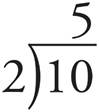 and don’t put the decimals back after dividing!
and don’t put the decimals back after dividing!
Practice Drill 12—Fractions as Decimals
|
Fraction |
Decimal |
Fraction |
Decimal |
|
0.5 |
|
0.2 |
|
|
|
0.4 |
|
|
|
0.6 |
|
0.25 |
|
0.8 |
|
0.75 |
|
0.125 |
Practice Drill 13—Percents
1.a) 30%
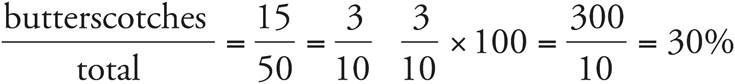
b) 40%
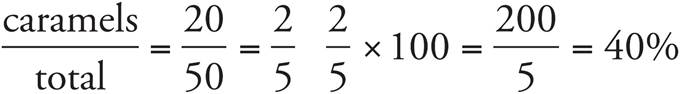
c) 10%
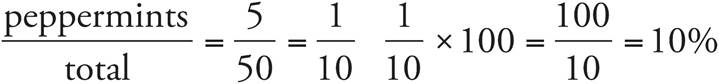
d) 20%
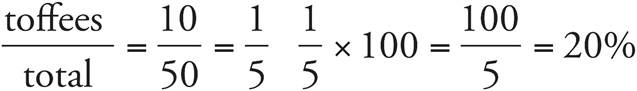
2.18%
100% = 75% + 7% + percentage of questions answered incorrectly
3.a) 20%
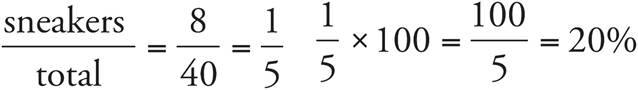
b) 30%
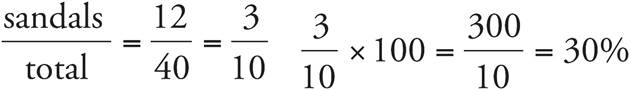
c) 40%
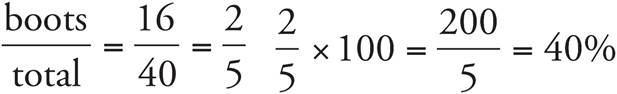
d) 10%
sneakers + sandals + boots + high heels = 100%
20% + 30% + 40% + h = 100%
h = 10%
e) 4
sneakers + sandals + boots + high heels = 40
8 + 12 + 16 + h = 40
h = 4
4.90%
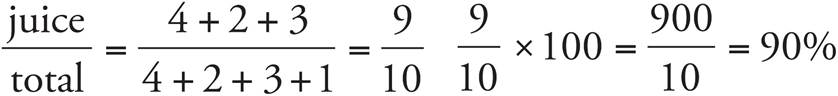
5.a) 48%
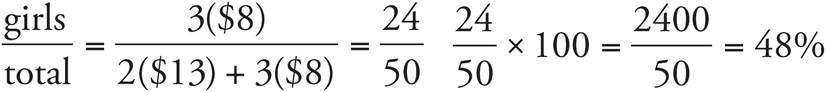
b) 52%
100% = girls + boys
100 = 48 + b
b = 52
Practice Drill 14—More Percents
|
Fraction |
Decimal |
Percent |
Fraction |
Decimal |
Percent |
|
0.5 |
50% |
|
0.2 |
20% |
|
|
|
|
0.4 |
40% |
|
|
|
|
0.6 |
60% |
|
0.25 |
25% |
|
0.8 |
80% |
|
0.75 |
75% |
|
0.125 |
12.5% |
1.21
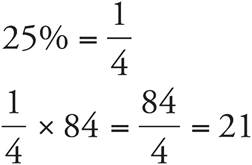
2.9
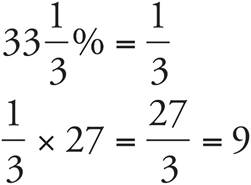
3.15
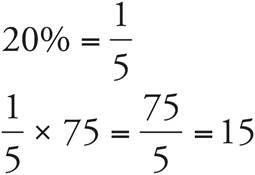
4.51
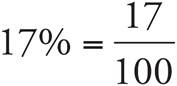
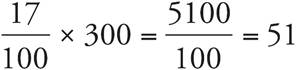
5.8
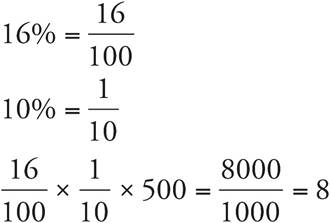
6.The sale price is $102.
15% of $120 = 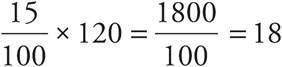 , and $120 − $18 = $102. The sale price is 85% of the regular price: 100% − 15% = 85%.
, and $120 − $18 = $102. The sale price is 85% of the regular price: 100% − 15% = 85%.
7.292
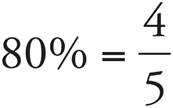
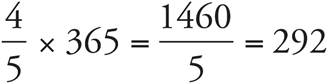
8.27
If she got 25% wrong, then she got 75% correct. 75% of 36 = 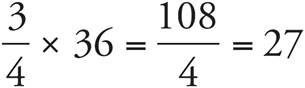 .
.
9.$72
If 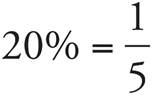 , then
, then 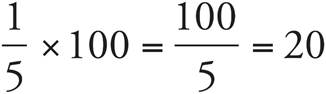 . The original price ($100) is reduced by $20, so the new price is $80. After an additional 10% markdown
. The original price ($100) is reduced by $20, so the new price is $80. After an additional 10% markdown 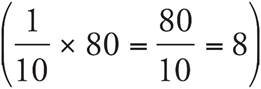 , the discounted price is reduced by $8, so the final sale price is
, the discounted price is reduced by $8, so the final sale price is ![]() .
.
Practice Drill 15—Percent Change
1.200%
The question is testing percent change since it asks by what percent did the temperature drop? To find percent change, use this formula: 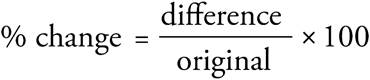 . The change in temperature was 20°: 10° — (—10°) = 20°. Since the question asks for the percent the temperature dropped, the larger number will be the original number. Thus, the equation should read
. The change in temperature was 20°: 10° — (—10°) = 20°. Since the question asks for the percent the temperature dropped, the larger number will be the original number. Thus, the equation should read 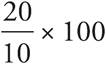 , which reduces to 2 × 100 = 200.
, which reduces to 2 × 100 = 200.
2.33%
The question is testing percent change since it asks by what percent did the patty increase? To find percent change, use this formula: 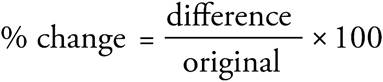 . The change in patty size is 4, which is given in the question. The new patty size is 16 oz, so the original patty size must have been 12 oz since 16 — 4 = 12. The equation will read
. The change in patty size is 4, which is given in the question. The new patty size is 16 oz, so the original patty size must have been 12 oz since 16 — 4 = 12. The equation will read 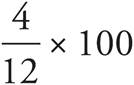 , which reduces to
, which reduces to 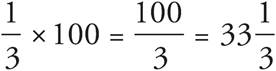 .
.
Practice Drill 16—Exponents and Square Roots
1.8
2 × 2 × 2 = 8
2.16
2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 16
3.27
3 × 3 × 3 = 27
4.64
4 × 4 × 4 = 64
5.9
92 = 9 × 9 or 81, so 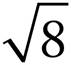 = 9.
= 9.
6.10
102 = 10 × 10 or 100, so 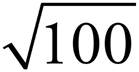 = 10.
= 10.
7.7
72 = 7 × 7 or 49, so 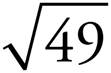 = 7.
= 7.
8.8
82 = 8 × 8 or 64, so 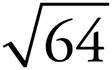 = 8.
= 8.
9.3
32 = 3 × 3 or 9, so 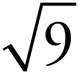 = 3.
= 3.
10.5
53 = 5 × 5 × 5 = 125, so 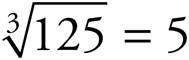 .
.
11.4
43 = 4 × 4 × 4 = 64, so 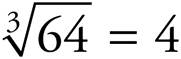 .
.
12.2
24 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 = 16, so 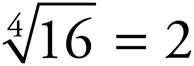 .
.
Practice Drill 17—More Exponents
1. 38
35 × 33 = 35+3 = 38
2. 79
72 × 77 = 72+7 = 79
3. 57
53 × 54 = 53+4 = 57
4. 153
1523 ÷ 1520 = 1523−20 = 153
5. 49
413 ÷ 44 = 413−4 = 49
6. 104
1010 ÷ 106 = 1010−6 = 104
7. 518
(53)6 = 53×6= 518
8. 836
(812)3 = 812×3 = 836
9. 925
(95)5 = 95×5 = 925
10. 228
(22)14 = 22×14 = 228
11. 2(3)4
The bases are different, so this cannot be simplified further.
12. 4x6
7 — 3 = 4 and the bases and exponents stay the same.
13. 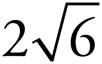
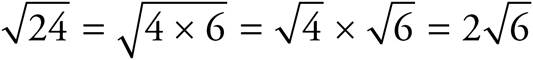
14. 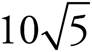
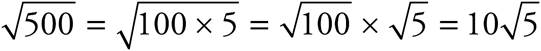
15. 12
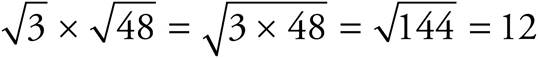
16. 5
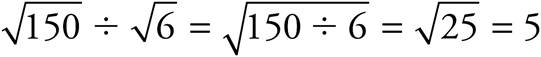
17. ![]()
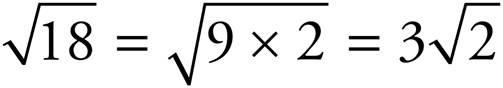 and
and 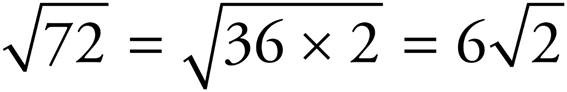 .
. 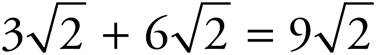
18. 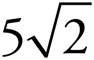
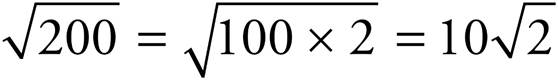 and
and 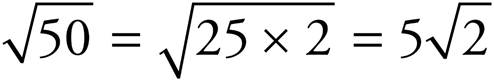 .
. ![]()
Review Drill 1—The Building Blocks
1. No
Remember, 2 is the smallest (and only even) prime number. 1 is NOT prime.
2. 9
1, 2, 4, 5, 10, 20, 25, 50, 100
3. —30
4. 140
5. 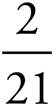
Multiply using Bowtie to get 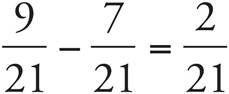 .
.
6. ![]()
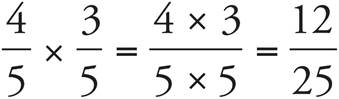
7. 4.08
Don’t forget there are a total of 2 digits to the right of the decimals.
8. 20
Multiply to get 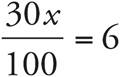 . Multiply both sides by 100 to get 30x = 600, and then divide both sides by 30 to get x = 20.
. Multiply both sides by 100 to get 30x = 600, and then divide both sides by 30 to get x = 20.
9. 1
15 = 1 × 1 × 1 × 1 × 1. Note: 1 to any power will always equal 1.
10. 4
42 = 4 × 4 or 16, so 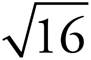 = 4.
= 4.
11. 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100
Algebra
Practice Drill 18—Solving Simple Equations
1.x = 12
35 — 12 = 23
2.y = 15
15 + 12 = 27
3.z = 28
28 — 7 = 21
4.x = 5
5 × 5 = 25
5.x = 3
18 ÷ 3 = 6
6.x = 11
3 × 11 = 33
7.y = 5
65 ÷ 5 = 13
8.z = 3
14 = 17 — 3
9.y = 48
![]() × 48 = 24
× 48 = 24
10.z = 71
136 + 71 = 207
11.x = 12
7 × 12 = 84
12.y = 12
12 ÷ 2 = 6
13.z = 45
45 ÷ 3 = 15
14.x = 18
14 + 18 = 32
15.y = 29
53 — 29 = 24
Practice Drill 19—Manipulating an Equation
1. 3
To isolate x, add x to both sides. Then subtract 8 from both sides. Check your work by plugging in 3 for x: 8 = 11 — 3.
2. 5
To isolate x, divide both sides by 4. Check your work by plugging in 5 for x: 4 × 5 = 20.
3. 6
To isolate x, add 20 to both sides. Then divide both sides by 5. Check your work by plugging in 6 for x: 5(6) — 20 = 10.
4. 7
To isolate x, subtract 3 from both sides. Then divide both sides by 4. Check your work by plugging in 7 for x: 4 × 7 + 3 = 31.
5. 4
To isolate m, add 3 to both sides. Subtract m from both sides. Then divide both sides by 2. Check your work by plugging in 4 for m: 4 + 5 = 3(4) — 3.
6. 8
To isolate x, divide both sides by 2.5. Check your work by plugging in 8 for x: 2.5 × 8 = 20.
7. 8
To isolate x, subtract 2 from both sides. Then divide both sides by 0.2. Check your work by plugging in 8 for x: 0.2 × 8 + 2 = 3.6.
8. ![]()
To isolate x, subtract 4 from both sides. Then divide both sides by 8. Check your work by plugging in ![]() for x:
for x: 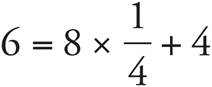 .
.
9. 7
To isolate x + y, divide both sides by 3. Check your work by plugging in 7 for x + y: 3(7) = 21.
10. 7
To isolate x + y, factor out a 3 from both terms on the left side: 3(x + y) = 21. Then divide both sides by 3. Check your work by plugging in 7 for x + y : 3(7) = 21. Note that this question and the previous question are really the same equation. Did you see it?
11. 7
To isolate y, subtract 100 from both sides. Then divide both sides by —5. Check your work by plugging in 7 for x: 100 — 5 × 7 = 65.
Practice Drill 20—Manipulating an Inequality
1.x > 4
To isolate x, divide both sides by 4. The sign doesn’t change!
2.x < —2
To isolate x, subtract 13 from both sides. Then divide both sides by —1. Since you divided by a negative number, flip the sign.
3.x > —5
First, combine like terms to get —5x < 25. Then divide both sides by —5. Since you divided by a negative number, flip the sign.
4.x > 4
To isolate x, add x to both sides. Subtract 12 from both sides. Then divide both sides by 3. The sign doesn’t change!
5.x < —7
To isolate x, add 3x to both sides. Subtract 7 from both sides. Then divide both sides by 3. The sign doesn’t change!
Practice Drill 21—Functions
1.26
Follow the directions and substitute 6 in for p. Since  p = 5p — 4,
p = 5p — 4,  6 = 5(6) — 4.
6 = 5(6) — 4.
2.35
Follow the directions and substitute 5 in for x. Since f(x) = 7x, f(5) = 7(5).
3.8
Follow the directions and substitute 10 in for p and 2 in for 1. Since p  q =
q = ![]() + 3, 10
+ 3, 10  2 =
2 = ![]() + 3.
+ 3.
4.5
Follow the directions and substitute 3 in for r. Since s(r) = r2 — 4, s(3) = 32 — 4.
Practice Drill 22—Foiling
1.x2 + 7 x + 12
FOIL: x × x = x2 , x × 3 = 3 x , 4 × x = 4 x , and 3 × 4 = 12. Add all these together to find that x2 + 3 x + 4 x + 12 = x2 + 7 x + 12.
2.x2 — 7 x + 12
FOIL: x × x = x2 , x × —3 = —3 x , —4 × x = —4 x , and —3 × —4 = 12. Add all these together to find that x2 − 3 x − 4 x + 12 = x2 − 7 x + 12.
3.x2 + x — 12
FOIL: x × x = x2, x × —3 = —3x, 4 × x = 4x, and —3 × 4 = —12. Add all these together to find that x2 — 3x + 4x — 12 = x2 + x — 12.
4.a2 — b2
FOIL: a × a = a2, a × —b = —ab, a × b = ab, and —b × b = —b2. Add all these together to find that a2 + ab — ab — b2 = a2 — b2.
5.a2 + 2ab + b2
FOIL: a × a = a2, a × b = ab, a × b = ab, and b × b = b2. Add all these together to find that a2 + ab + ab + b2 = a2 + 2ab + b2.
6.a2 — 2ab + b2
FOIL: a × a = a2, a × —b = —ab, —a × b = —ab, and —b × —b = b2. Add all these together to find that a2 — ab — ab + b2 = a2 — 2ab + b2.
7.25
FOIL out (x — y)2 to find x2 — 2xy + y2. Since x2 + y2 = 53, substitute 53 to find 53 — 2xy. Substitute 14 in for xy: 53 — 2(14) = 53 — 28 = 25.
8.(x + 6)(x + 7)
Factor into two binomials. Since x2 is the first term and both signs are positive, place an x and an addition sign in each of the binomial parentheses to find (x + )(x + ). Now, find two factors of 42 that also add up to 13. 6 and 7 work, and since both binomials contain addition signs, the order does not matter.
9.(y + 2)(y — 5)
Factor into two binomials. Since y2 is the first term and the signs are opposite, place a y and opposite signs in each of the binomial parentheses to make (y + )(y — ). Now, find two factors of 10 that also add up to —3. 2 and —5 work, so place 2 in the binomial with the addition sign and 5 next to the subtraction sign.
10.(x — 5)(x — 7)
Factor into two binomials. Since x2 is the first term, the last term is positive and the middle term is negative, place an x and a subtraction sign in each of the binomial parentheses to make (x — )(x — ). Now, find two factors of 35 that also add up to 12. 5 and 7 work, and since both binomials contain subtraction signs, the order does not matter.
11.(y + 8)(y + 3)
Factor into two binomials. Since y2 is the first term and both signs are positive, place a y and an addition sign in each of the binomial parentheses to find (y + )(y + ). Now, find two factors of 24 that also add up to 11. 3 and 8 work, and since both binomials contain addition signs, the order does not matter.
12.(a + 2)(a — 7)
Factor into two binomials. Since a2 is the first and both signs are negative, place an a and opposite signs in each of the binomial parentheses to make (a + )(a — ). Now, find two factors of 14 that also add up to —5. 2 and —7 work, so place 2 in the binomial with the addition sign and 7 next to the subtraction sign.
13.(b — 5)(b — 6)
Factor into two binomials. Since b2 is the first term, the middle term is negative and the last term is positive, place a b and a subtraction sign in each of the binomial parentheses to make (b — )(b — ). Now, find two factors of 30 that also add up to 11. 5 and 6 work, and since both binomials contain subtraction signs, the order does not matter.
14.(k + 9)(k + 7)
Factor into two binomials. Since k2 is the first term and both signs are positive, place a k and an addition sign in each of the binomial parentheses to find (k + )(k + ). Now, find two factors of 63 that also add up to 16. 9 and 7 work, and since both binomials contain addition signs, the order does not matter.
Practice Drill 23—Translating and Solving Percent Questions
1.12
Translation: 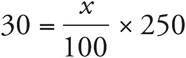 . To solve, simplify the right side:
. To solve, simplify the right side: 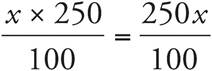 , which reduces to
, which reduces to 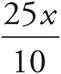 . Multiply both sides by 10, and then divide both sides by 25. Check your work by plugging in 12 for x.
. Multiply both sides by 10, and then divide both sides by 25. Check your work by plugging in 12 for x.
2.24
Translation: 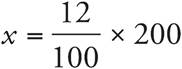 . To solve:
. To solve: 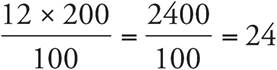 .
.
3.5
Translation: 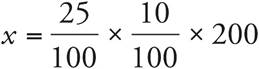 . To solve, reduce the right side:
. To solve, reduce the right side: 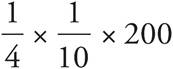 . Then simplify:
. Then simplify: 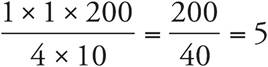 .
.
4.80
Translation: 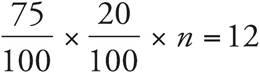 . To solve, reduce the left side:
. To solve, reduce the left side: 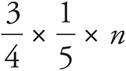 . Then simplify:
. Then simplify: 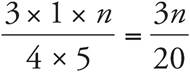 . Multiply both sides by 20, and divide both sides by 3. Check your work by plugging in 80 in for n.
. Multiply both sides by 20, and divide both sides by 3. Check your work by plugging in 80 in for n.
5.125
Translation: 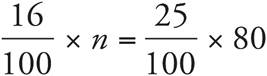 . To solve, reduce both sides to get
. To solve, reduce both sides to get 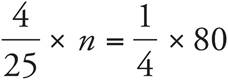 . Then, multiply to get
. Then, multiply to get 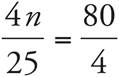 . Next, cross-multiply to get 16n = 2,000. Finally, divide both sides by 16. Check your work by plugging in 125 for n.
. Next, cross-multiply to get 16n = 2,000. Finally, divide both sides by 16. Check your work by plugging in 125 for n.
6.60
Translation: 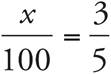 . To solve, cross-multiply to get 5x = 300, and then divide both sides by 5. Check your work by plugging in 60 for x.
. To solve, cross-multiply to get 5x = 300, and then divide both sides by 5. Check your work by plugging in 60 for x.
7.40
Translation: 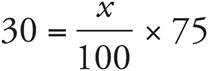 . To solve, simplify the right side:
. To solve, simplify the right side: 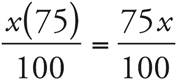 , which reduces to
, which reduces to ![]() . Multiply both sides by 4, and divide both sides by 3. Check your work by plugging in 40 for x.
. Multiply both sides by 4, and divide both sides by 3. Check your work by plugging in 40 for x.
8.2.64 or 2 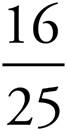 or
or 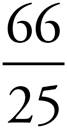
Translation: 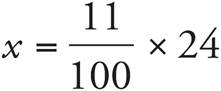 . To solve,
. To solve, 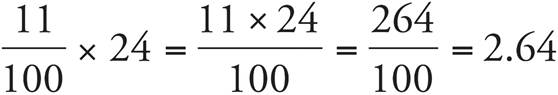 .
.
9.200
Translation: 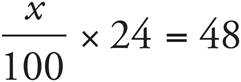 . To solve, simplify the left side:
. To solve, simplify the left side: 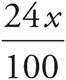 , which reduces to
, which reduces to ![]() . Then multiply both sides by 25, and divide both sides by 6. Check your work by plugging in 200 for x.
. Then multiply both sides by 25, and divide both sides by 6. Check your work by plugging in 200 for x.
10.2
Translation: 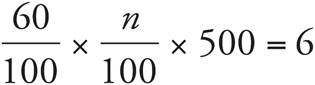 . To solve, reduce the fraction to
. To solve, reduce the fraction to ![]() and simply the left side:
and simply the left side: 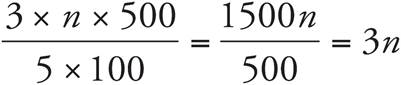 . Then divide both sides by 3. Check your work by plugging in 2 for n.
. Then divide both sides by 3. Check your work by plugging in 2 for n.
Practice Drill 24—Averages
1.108
Use an Average Pie to solve this question. Place 3 in the # of items and 18 in for the average . Multiply these numbers to find the total, which is 54. The question asks for twice the sum, which is the same as twice the total, so 2 × 54 = 108.
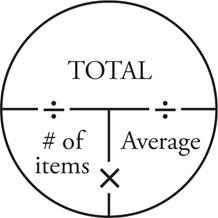
2.23
Use two Average Pies to organize the information in this question—every time you see the word average, draw an Average Pie. The first pie represents the information about the boys: 4 boys average 2 projects each, so place 4 in the # of items place and 2 in the average place. To find the total number of projects the boys complete, multiply 4 and 2 to find a total of 8 projects. Repeat this same process with the girls in the second pie. The 5 girls average 3 projects each, so place these numbers in their respective places in the Average Pie, and multiply to find a total of 15 projects. The question asks for the total number of projects in the class, so 8 + 15 = 23.
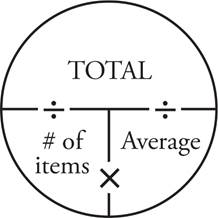
3.99
First, add the three scores to find Catherine’s current point total. 84 + 85 + 88 = 257. Next, make an Average Pie with 4 in the # of items place since there will be a fourth test, and 89 as the desired average. Multiply 4 × 89 to find a total of 356. Subtract the totals to find that 356 — 257 = 99. This means that she must score a 99 on the fourth test to raise her average to an 89.
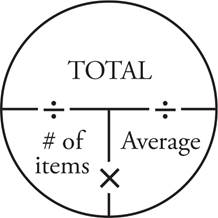
4.100
Use two Average Pies to organize the information in this question—every time you see the word average, draw an Average Pie. There are 6 students with an average test score of 72. Place 6 in the # of items place and 72 in the average place. Find the total number of points by multiplying 6 × 72 = 432. Make a separate Average Pie for the next portion of the question. If a seventh student joins the class, the # of items place now contains 7, and the desired average is 76. Multiply these together to find that 7 × 76 = 532. The difference between 532 and 432 is 100, so the seventh student must score 100 to change the average to 76.
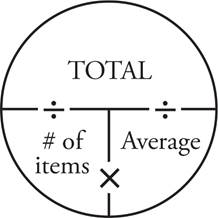
More Practice: Lower Level
5.2
Use an Average Pie to solve this question. List the number of doughnuts Fatima ate each day: Monday = 2, Tuesday = 4, Wednesday = 2, Thursday = 4, Friday = 2, Saturday = 0, and Sunday = 0. The question asks for the average number of doughnuts she ate over the course of all 7 days, so add all the doughnuts she ate: 2 + 4 + 2 + 4 + 2 + 0 + 0 = 14. Put 14 in the total spot in your Average Pie. The # of items is 7 since the question asks about the whole week. Finally, divide these two numbers to get the average: 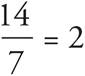 .
.
6.53 or 54
When you see the word average , draw an Average Pie. To find the average for the whole trip, find the total number of miles: 240 mi + 350 mi = 590 mi. Put 590 in the total part of the Average Pie. Then find the total number of hours Merry drove: 4 hrs + 7 hrs = 11 hrs. 11 will go in the # of items spot. Next, divide to find the average: 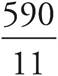 . Since the question says “approximate”, there’s no need to figure out the exact decimal.
. Since the question says “approximate”, there’s no need to figure out the exact decimal.
7.15
When you see the word average, draw an Average Pie. To find the average number of comic books, start by finding the total number: 11 + 14 + 16 + 19 = 60. Put 60 in the total part of the Average Pie. Then put 4, the number of friends, into the # of things spot. Next, divide to find the average: 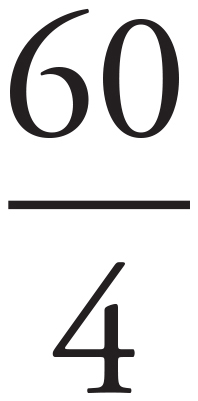 = 15.
= 15.
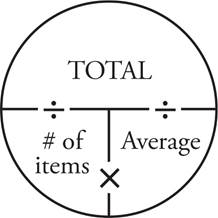
More Practice: Middle and Upper Levels
8.30
Use two Average Pies to organize the information in this question—every time you see the word average, draw an Average Pie. The question states that Michael scored an average of 24 points over his first 5 basketball games. Therefore, place 24 in the average place of the pie, and 5 in the # of items place. Multiply these numbers together to find that Michael scored a total of 120 points over the five games. To find how many points he must score on his sixth game to bring his average up to 25, use the second Average Pie to plug in the given information. Write 6 in the # of items place to account for all six games, and 25 in the average place since that’s the desired average. Multiply these numbers to find he must score a total of 150 points over the entire 6 games. The difference between 150 and 120 is 30, so Michael must score 30 points in the sixth game to raise his average to 25.
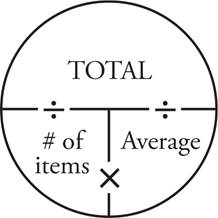
9.7
The problem gives information about the weekly amount of rain, but the question asks about the daily amount instead. The daily amount will be the average (i.e., the amount of rain per day). Place 245 in the total spot of the first Average Pie and 7 in the # of items place. That gives you an average of 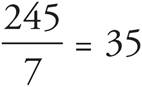 , which is the average daily amount for the current year. Do the same for the previous year in a second Average Pie. This time, 196 goes in the total spot and 7 goes in the # of items place. That equals an average of
, which is the average daily amount for the current year. Do the same for the previous year in a second Average Pie. This time, 196 goes in the total spot and 7 goes in the # of items place. That equals an average of 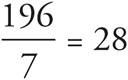 . The question asks for how many more inches , so you will need to subtract the two daily amounts of rain: 35 — 28 = 7.
. The question asks for how many more inches , so you will need to subtract the two daily amounts of rain: 35 — 28 = 7.

10.270
Since the question mentions the mean, create an Average Pie. Joe wants to have an average of 230 or more, so place 230 in the average spot of the pie. In the # of items place, write in 5 because he has already read 4 books that were 200, 200, 220, and 260 pages long, and he is going to read one more. Multiply to find the total number of pages he must read: 5 × 230 = 1,150. He has already read 200 + 200 + 220 + 260 = 880 pages, so find the difference between these two totals to see how many pages long the fifth book must at least be: 1,150 — 880 = 270.
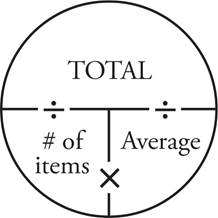
Practice Drill 25—Word Problems
1.4 quarts
Set up a proportion: 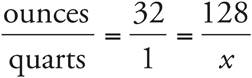 . Then cross-multiply to get 32(x) = 128. Divide both sides by 32, and x = 4.
. Then cross-multiply to get 32(x) = 128. Divide both sides by 32, and x = 4.
224 ounces
Set up a proportion: 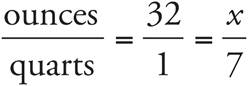 . Then cross-multiply to get 32(7) = x, and x = 224.
. Then cross-multiply to get 32(7) = x, and x = 224.
2.6 hours
Set up a proportion: 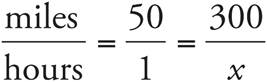 . Then cross-multiply to get 50x = 300. Divide both sides by 50, and x = 6.
. Then cross-multiply to get 50x = 300. Divide both sides by 50, and x = 6.
3.44
Start with the given age: Rufus’s. If Rufus is 11, then find Fiona’s age. Fiona is twice as old as Rufus translates to Fiona = 2(Rufus) or f = 2(11), so Fiona is 22. Next find Betty’s age. Betty is twice as old as Fiona translates to Betty = 2(Fiona) or B = 2(22). Therefore, Betty is 44.
4.5
Translate the parts of the question. This year’s sales = 1,250, how many times greater than means to divide, and last year’s sales = 250. Thus, 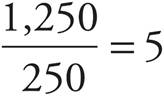 .
.
5.120
Translate the first part of the problem: of means to multiply and the total students = 500. So, the number of freshman is 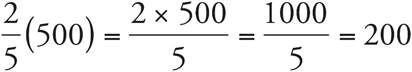 . Now, translate the second part of the problem: of means to multiply and all the freshmen = 200. Therefore, the number of freshmen girls is
. Now, translate the second part of the problem: of means to multiply and all the freshmen = 200. Therefore, the number of freshmen girls is 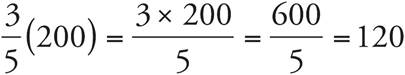 .
.
Geometry
Practice Drill 26—Squares, Rectangles, and Angles
1.115°
65° + x° = 180°
2.100°
45° + x° + 35° = 180°
3.36
4 + 4 + 4 + 4 = 16. Its area is also 16. 42 = 16. The perimeter of PQRS is 16.
4.21
7 + 3 + 7 + 3 = 20. Its area is 21. 7 × 3 = 21. The perimeter of ABCD is 20.
5.9
(12 ÷ 4 = 3). Therefore, the area is 32 = 9. The area of STUV is 9. If the perimeter is 12, then one side of the square is 3.
6.36
The perimeter of DEFG is 36. If the area is 81, then one side of the square is 9 (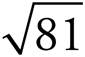 = 9). Therefore, the perimeter is 9 + 9 + 9 + 9 = 36.
= 9). Therefore, the perimeter is 9 + 9 + 9 + 9 = 36.
7.24
The area of JKLM is 24. If the perimeter is 20, then 4 + l + 4 + l = 20. So the length (the other side) of the rectangle is 6. Therefore, the area is 6 × 4 = 24.
8.22
The perimeter of WXYZ is 22. If the area is 30, then 6 × w = 30. So the width (the other side) of the rectangle is 5. Therefore, the perimeter is 6 + 5 + 6 + 5 = 22.
9.24
V = lwh = 2 × 4 × 3 = 24.
Practice Drill 27—Triangles
1.45°
Since two sides (legs) of the triangle are both 3, the angles that correspond to those sides are also equal to each other. 180° — 90° = 90°. Therefore, each angle is 45°, so x = 45°.
2.70°
Since sides PQ and QR are equal, then ∠QPR and x° are also equal to each other. 180° — 40° = 140°. Thus, divide 140° by 2 to find that each remaining angle is 70°. So x = 70°.
3.6
Plug the base and height into the area formula for a triangle: 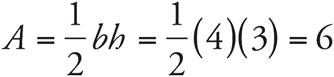 .
.
4.12
In this case, count the height and base of the triangle by counting off the ticks on the coordinate plane. The height is 6 and the base is 4, which means that 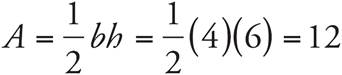 .
.
5.12
Plug the base and height into the area formula for a triangle: 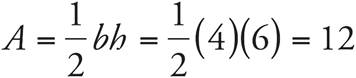 .
.
6.WXZ = 5
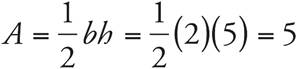
ZXY = 15
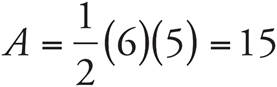
WXY = 20
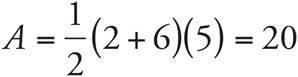
7.4.8
These are similar triangles since all the angles are the same. Set up a proportion to solve: 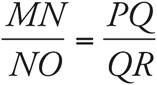 , so
, so 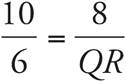 . Cross-multiply to get 10(QR) = 6(8). Divide both sides by 10, and QR = 4.8.
. Cross-multiply to get 10(QR) = 6(8). Divide both sides by 10, and QR = 4.8.
8.DE = 8
Since this is a right triangle, use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing side length: a2 + b2 = c2, so a2 + 62 = 102. Subtract 36 from both sides and a2 = 64. Take the square root of both sides, and a (or DE) = 8.
9.9.6
These are similar triangles since all the angles are the same. Set up a proportion to solve: 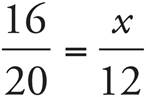 . Cross-multiply to get 16(12) = 20(x). Divide both sides by 20, and x = 9.6.
. Cross-multiply to get 16(12) = 20(x). Divide both sides by 20, and x = 9.6.
10.26
Remember that all angles in a rectangle are right angles. This diagonal (AC) cuts the rectangle into two right triangles, so use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the missing side length: a2 + b2 = c2, so 102 + 242 = c2, and c (or AC) = 26.
11.40
First, use the right triangle to find AD, which is one side of the square ABCD. 82 + 62 = c2, so c = 10. Since all sides of a square are equal, the perimeter is 10 + 10 + 10 + 10 = 40 (or 10(4) = 40).
12.2.4
These are similar triangles since all the angles are the same. Set up a proportion to solve: 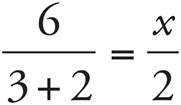 . Cross-multiply to get 5x = 6(2). Divide both sides by 5, and x = 2.4.
. Cross-multiply to get 5x = 6(2). Divide both sides by 5, and x = 2.4.
Practice Drill 28—Circles
1.Circumference = 10π. Area = 25π.
Plug the radius into the circumference formula for a circle: C = 2πr = 2π(5) = 10π. Plug the radius into the area formula for a circle: A = πr2 = π(5)2 = 25π.
2.16π
Plug the radius into the area formula for a circle: A = πr2 = π(4)2 = 16π.
3.16π
Since d = 2r, the radius is 4(8 = 2r). Plug the radius into the area formula for a circle: A = πr2 = π(4)2 = 16π. Note: this is really the same circle as the previous question.
4.3
Remember, you can find the radius from a circle’s area by getting rid of π and taking the square root of the number, in this case 9.
5.6
Find the radius from the circle’s area by getting rid of π and taking the square root of 9. Then multiply the radius by 2 to find the diameter.
6.10π
Find the radius from the circle’s area by getting rid of π and taking the square root of 25. Then, plug the radius into the circumference formula for a circle: C = 2πr = 2π(5) = 10π.
Practice Drill 29—3-D Shapes
1.128π
Plug the radius and height into the volume formula for a cylinder: V = πr2h = π(4)2(8) = 128π.
2.1,000
Plug the side length into the volume formula for a cube: V = s3 = 103 = 1,000.
3.216
Plug the length, width, and height into the volume formula for a rectangular box: V = lwh = 12 × 3 × 6 = 216.
4.162
First, find the volume of the cube: V = s3 = 63 = 216. Next, to find the remaining liquid needed to completely fill the cube, subtract the volume of liquid already poured into it: 216 — 54 = 162.
5.12
One way to solve this problem is to divide the length, width, and height into segments of 2. The length is 8, so 4 cubes could fit along the length of the rectangular box since each cube has a side length of 2. The width of the box is 2, so only 1 cube could fit along the width of the box. That means the bottom layer of the box could hold 4 cubes (4 cubes across by 1 cube deep). The height of the box is 6, so you could stack 3 cubes on top of each other to fill the box. If each layer has 4 boxes and 3 layers of cubes can be stacked, then a total of 12 cubes can fit into the box (4 boxes per layer times 3 layers equals 12 boxes).
6.48π
First, find the volume of the cylinder: V = πr2h = π(4)2(9) = 144π. Since the grain fills only a third of the cylinder, then find ![]() of the volume, or
of the volume, or 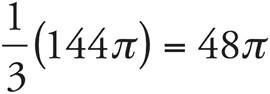 . Just treat the π like a variable in questions like these.
. Just treat the π like a variable in questions like these.
Coordinate Geometry
Practice Drill 30—Coordinate Geometry
1. 4
The slope of a perpendicular line is its negative reciprocal. The reciprocal of ![]() is 4, and since the original slope was negative, its reciprocal must be positive.
is 4, and since the original slope was negative, its reciprocal must be positive.
2. —5
The formula of a line is y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. The y-intercept is —5, since this is where it crosses the y-axis. Therefore, the formula will read y = mx — 5. Now, either use the slope formula to find the slope, or simply plug in a point to x and y to find m. Try the point (—1, 0): 0 = m(—1) — 5. Multiply m by —1 to find that 0 = —m — 5. Add 5 to both sides to isolate m, so 5 = —m. Multiply by —1 on both sides to get m alone, so —5 = m.
3. (—4, 8)
Plot the points to see what these points look like on the xy-coordinate plane:
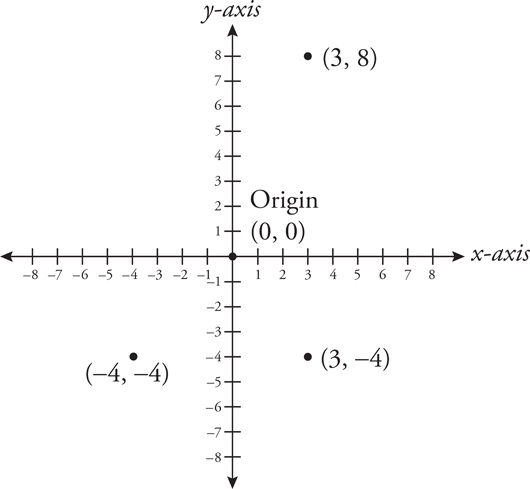
The points start to outline a rectangle, which is a type of parallelogram. Since rectangles create right angles, the missing point should be in the top left corner, in line with the y-value of (3, 8). The point will also be in line with the x-value of (—4, —4). Therefore, the point will be (—4, 8).
4. 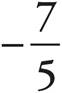
Use the slope formula and plug in the points given. To distinguish the points, arbitrarily call one of them point 1 and point 2. For instance, (—2, 12) = (x1, y1), and (3, 5) = (x2, y2). Now, use the slope formula 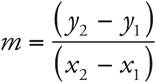 . (5 — 12) ÷ (3 — (—2)) = —
. (5 — 12) ÷ (3 — (—2)) = —![]() .
.
5.A
The slope of line k is positive because it slopes upward from left to right. The slope of a line that is parallel will be the same as that of k, so it will be positive as well. The slope of a line perpendicular will be the negative reciprocal. Even though the slope of the line is not given in the question, the slope of the perpendicular line will have to be negative. Therefore, the slope of the parallel line will always be greater.
Practice Drill 31—Trigonometry
1. 1.5 tan 23°
To find the length of the shadow on the ground, label the figure. Samin is 1.5 meters, and let the shadow length on the ground (the other leg of the triangle) equal x meters. Since the sides are the opposite and adjacent sides to the angle, 23°, use tangent: tan 23º = 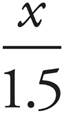 . Multiply by 1.5 on either side to isolate x to find that 1.5 tan 23º = x.
. Multiply by 1.5 on either side to isolate x to find that 1.5 tan 23º = x.
2. ![]()
The cosine is the adjacent side over the hypotenuse. The side adjacent to x° is side c. Therefore, the cosine is c divided by the hypotenuse, a.
3. 50 sin 5°
Since the hypotenuse is given and h is opposite of the 5°, use sine for a measurement: sin 5° = 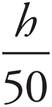 . Multiply by 50 on each side to find that 50 sin 5° = h.
. Multiply by 50 on each side to find that 50 sin 5° = h.
4. ![]()
Label the figure using the cosine information: the leg adjacent to x° is 24 and the hypotenuse is 25. To find sine of y°, use SOH of SOHCAHTOA. Therefore, sin y° equals the opposite divided by the hypotenuse. The side opposite y° is, and the hypotenuse is , so sin y° = 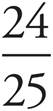 .
.
5. ![]()
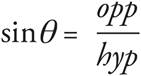 , so the opposite is 4, but the hypotenuse is unknown. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the hypotenuse: a2 + b2 = c2, in which c is the hypotenuse and a and b are the legs. Therefore, 32 + 42 = c2. Simplify the exponents to find that 9 + 16 = c2 = 25. Take the square root of 25 to find the hypotenuse, which is 5. Now, plug 5 into the sine equation to find that
, so the opposite is 4, but the hypotenuse is unknown. Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the hypotenuse: a2 + b2 = c2, in which c is the hypotenuse and a and b are the legs. Therefore, 32 + 42 = c2. Simplify the exponents to find that 9 + 16 = c2 = 25. Take the square root of 25 to find the hypotenuse, which is 5. Now, plug 5 into the sine equation to find that 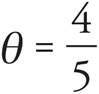 .
.
Practice Drill 32—Probability
1.27
The question asks for the number of marbles in the basket. The probability of not selecting a blue marble is ![]() , so the probability of selecting a blue marble is
, so the probability of selecting a blue marble is 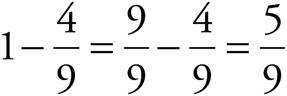 . Use the probability formula:
. Use the probability formula: 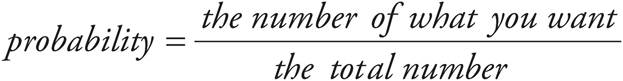 . The probability is
. The probability is ![]() , and the number of what you want is the number of blue marbles, which is 15. The question asks for the total number, so set this equal to x to get
, and the number of what you want is the number of blue marbles, which is 15. The question asks for the total number, so set this equal to x to get 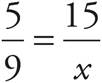 . Cross-multiply to get 5 x = 135. Divide both sides by 5 to get x = 27.
. Cross-multiply to get 5 x = 135. Divide both sides by 5 to get x = 27.
2. ![]()
The question asks for the probability that the fruit selected will be an apple or a kiwi, so get the sum of the probabilities that the fruit will be an apple and that the fruit will be a kiwi. There is a total of 4 + 6 + 5 = 15 pieces of fruit. There are 4 apples, so the probability that the fruit is an apple is 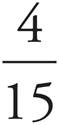 . There are 6 kiwis, so the probability that the fruit is a kiwi is
. There are 6 kiwis, so the probability that the fruit is a kiwi is ![]() . Therefore, the probability that the fruit is an apple or a kiwi is
. Therefore, the probability that the fruit is an apple or a kiwi is 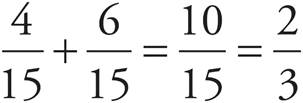 .
.
3. ![]()
The question asks for the probability that both cookies are pecan, so multiply the probabilities that each individual cookie will be pecan. There are 4 pecan cookies and 2 + 4 + 7 + 3 = 16 total cookies, so the probability that the first cookie will be pecan is 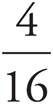 . Once one pecan cookie is removed, there are 3 remaining pecan cookies and 15 total cookies remaining, so the probability that the second cookie will be pecan is
. Once one pecan cookie is removed, there are 3 remaining pecan cookies and 15 total cookies remaining, so the probability that the second cookie will be pecan is 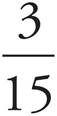 . Multiply the two to get
. Multiply the two to get 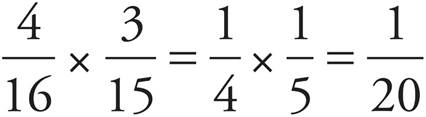 .
.
4. 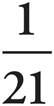
On the first trial, Sandy chooses a chocolate chip cookie, which has a probability of 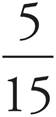 . On the second trial, she chooses a red velvet cookie. There are 2 red velvet cookies, but now there are only 14 cookies remaining in the jar to choose from. The probability for the second trial is
. On the second trial, she chooses a red velvet cookie. There are 2 red velvet cookies, but now there are only 14 cookies remaining in the jar to choose from. The probability for the second trial is 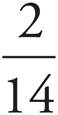 . Multiply these together since these are independent of each other:
. Multiply these together since these are independent of each other: 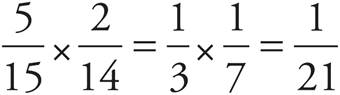 .
.
Practice Drill 33—Charts and Graphs
1.E
First, find what District A spent in 2017: $400,000 (pay attention to the note below the table: the numbers are in thousands of dollars). Look for double this amount. $800,000 is listed in the table for the value in 2021 for District E.
2.E
Add across to find which district spent the most, keeping in mind that these are all in the thousands (though this doesn’t really matter to find the largest sum). District E has the largest sum: $600,000 + $800,000 = $1,400,000.
3.$800,000
Remember that these numbers are in the thousands. Add down to find the sum of the values in 2017: $1,800,000. Do the same with the values in 2021 to find a sum of $2,600,000. Find the difference of these values: $2,600,000 — $1,800,000 = $800,000.
4.Abe and Dave
Check the graph. Carl owns 5 cellphones, so the other two people together must own a total of 5 cellphones.
5.Ben
To find which student owns one-fourth of all the cellphones, first add all the cellphones to find a total. Your work from the previous question will help! Abe = 2, Ben = 4, Carl = 5, Dave = 3, and Ed = 2, which yields a total of 16 cellphones. ![]() of 16 is
of 16 is 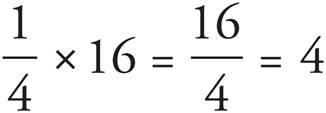 , so Ben is the student who has 4 cellphones.
, so Ben is the student who has 4 cellphones.
6.$84
To find Matt’s earnings for the week, first add up all his hours and then multiply by his hourly salary ($6/hour). He works 3.5 + 4 + 3.5 + 3 = 14 hours over the week, so 14 × 6 = 84.
7.3.5
Remember, if you see the word average , you can use an Average Pie. The previous question helped you find the total number of hours Matt worked: 14. Put that number in the total place. He worked 4 days—note the question says on the days he worked, not the number of days in a week. Put 4 in the # of items place. Divide these two numbers to find the average: 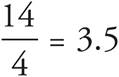 . If you’re pressed for time, instead of doing the long division, let the answer choices help! Since 14 is not divisible by 4, eliminate all the integers.
. If you’re pressed for time, instead of doing the long division, let the answer choices help! Since 14 is not divisible by 4, eliminate all the integers.
8.25
One way to solve this problem is to translate the words into math: The hours he worked on Monday is 3.5, accounted for is equals, what percent is 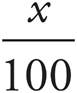 , and the total hours he worked is 14. The equation is
, and the total hours he worked is 14. The equation is 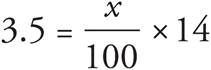 . Simplify the right side:
. Simplify the right side: 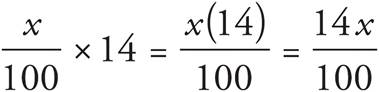 . Multiply both sides by 100 to get 350 = 14 x. Divide both sides by 14, and x = 25. You can also find a percent by dividing the desired amount by the total amount: Matt worked 3.5 hours on Monday and a total of 14 hours, so
. Multiply both sides by 100 to get 350 = 14 x. Divide both sides by 14, and x = 25. You can also find a percent by dividing the desired amount by the total amount: Matt worked 3.5 hours on Monday and a total of 14 hours, so 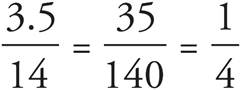 , or 25%.
, or 25%.
Review Drill 2—The Building Blocks
1.45
Translate the problem: 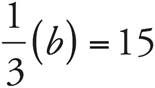 . Multiply both sides by 3, and b = 45. Check your work by plugging in 45 for b:
. Multiply both sides by 3, and b = 45. Check your work by plugging in 45 for b: 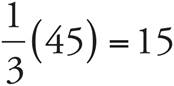 .
.
2.8
To isolate x, add 7 to both sides. Then divide both sides by 7. Check your work by plugging in 8 for x: 7(8) — 7 = 49.
3.10
To isolate y, divide both sides by 4. Then add 5 to both sides. Check your work by plugging in 10 for y: 4(10 — 5) = 20.
4.x < 8
To isolate x, subtract 1 from both sides. Then divide both sides by 8. The sign doesn’t change!
5.160
Translation: 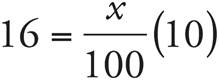 . To solve, simplify the right side:
. To solve, simplify the right side: 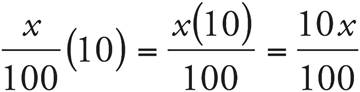 , which reduces to
, which reduces to 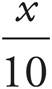 . Then, multiply both sides by 10. Check your work by plugging in 160 for x.
. Then, multiply both sides by 10. Check your work by plugging in 160 for x.
6.75
Translation: 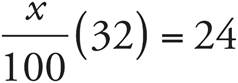 . To solve, simplify the left side of the equation:
. To solve, simplify the left side of the equation: 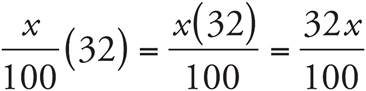 , which reduces to
, which reduces to ![]() . Then multiply both sides by 25, and divide both sides by 8. Check your work by plugging in 75 for x.
. Then multiply both sides by 25, and divide both sides by 8. Check your work by plugging in 75 for x.
7.21
Plug the base and height into the area formula for a triangle: 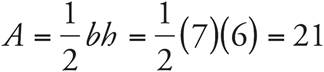 .
.
8.14
Find the radius from a circle’s area by getting rid of π and taking the square root of 49. Then multiply the radius by 2 to find the diameter.
9.6
Find the radius from a circle’s circumference (C = 2πr) by getting rid of π from both sides (they cancel out), which leaves 12 = 2r. Divide both sides by 2. Check your work by plugging in 6 for the radius.
10.25π Be careful not to just fill in a familiar formula with the given numbers. Here, you aren’t given r. Instead, you’re given the diameter. Since d = 2r, the radius is 5 (10 = 2r). Plug the radius into the area formula for a circle: A = πr2 = π(5)2 = 25π.