Real Grammar - Susan Conrad, Douglas Biber 2009
Verbs with Two Objects
Unit 9 Tell me that story
What have you learned from your grammar textbook?
Many verbs can occur with two objects. The direct object (DO) identifies the thing influenced by the action of the verb, while the indirect object (IO) identifies the person who received the action. The indirect object can come first or second.
When the indirect object comes first, this is the grammatical pattern: V + IO + DO.
![]()
When the indirect object comes second, we use the preposition to or for : V + DO + to/for + IO.
![]()
What does the corpus show?
A
Many of the most common verbs in English can occur with two objects.

• Would you bring me a cup of coffee?
• He gave her a letter.
• I could show him my map.
• I bought a dress for you.
• She sold the house to Wally.
B
Several of these verbs usually occur with special grammatical patterns.
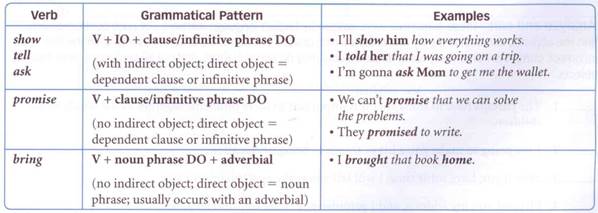
C
The order of the two objects is usually determined by the length of each object. The longer object goes last.
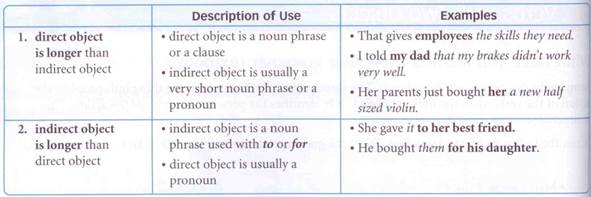
Be careful! If both objects are pronouns, the order is: V + DO + to/for + IO.
• Give that to me.
Activities
1 Notice in context: Read the conversation. Some of the boldfaced verbs have one object, and some have two objects, underline the direct object and circle the indirect object, if there is one.
Discussing a used car that stopped working.
Bill: They sold me their Volkswagen van and I’m not driving it right now because it’s not running well. They told me they’d stop by sometime tonight and look at it.
Janet: Hmm, why did you buy it if it’s not working?
Bill: Well, they brought it over here and they said it’s running real good.
Janet: Hmm. Maybe somebody had been working on it. Um, so you already paid for it?
Bill: Most of it. Uh, I promised to pay more, but I don’t know ...
Janet: Yeah, you should ask them what they think about it now that it’s not running.
2 Analyze and edit: These sentences were written by English-language learners. For each boldfaced verb, find the object(s) and decide if they are in the correct order. If the sentence is correct, write C on the line. If it is incorrect, correct it. Remember, some direct objects may be entire clauses, and not all sentences have indirect objects.
![]()
2. I am going to make you a list of things to bring on vacation.
3. Now if you have some time, I will tell where the apartment is to you.
4. I’ll send you my address, and I promise you to do well and be good.
5. My friends might bring some gifts and cards to me.
6. I asked if it’s true that he never watched television to the prisoner.
3 Practice the structure: Each sentence contains both a direct and an indirect object (in parentheses), but they may be out of order. Rewrite the sentence on the line. Make sure the objects are in the correct order.
1. She showed (how to boil the meat I them).
She showed them how to boil the meat.
2. Arnold picks apples and brings (them / to his family).
3. She told (that she was afraid of driving in the snow I him).
4. I bought (for him I it).
5. I asked (if this was the correct address I them).
4 Practice conversation: Get to know a classmate better. Ask each other questions about family, school, leisure activities, etc. Use the verb in parentheses in each question and answer. Include both a direct and an indirect object in each answer (unless the verb has a special grammatical structure without one). After you talk, write down your questions and answers.
(give) A: What, do you give your mother for her birthday?
B: Usually I give her flowers.
(show) A: ...
B: ...
(bring) A: ...
B: ...
(send) A: ...
B: ...
(tell) A: ...
B: ...
(ask) A: ...
B: ...